CDP vs. CRM: Understanding the Difference in 2025
Introduction
As customer data becomes the foundation of modern marketing, businesses often struggle to decide between a CDP and a CRM — or how to use both effectively.
While both systems manage customer data, their purpose, structure, and outcomes are entirely different.
Let’s break down their differences, use cases, and how they can complement each other in a data-driven marketing ecosystem.
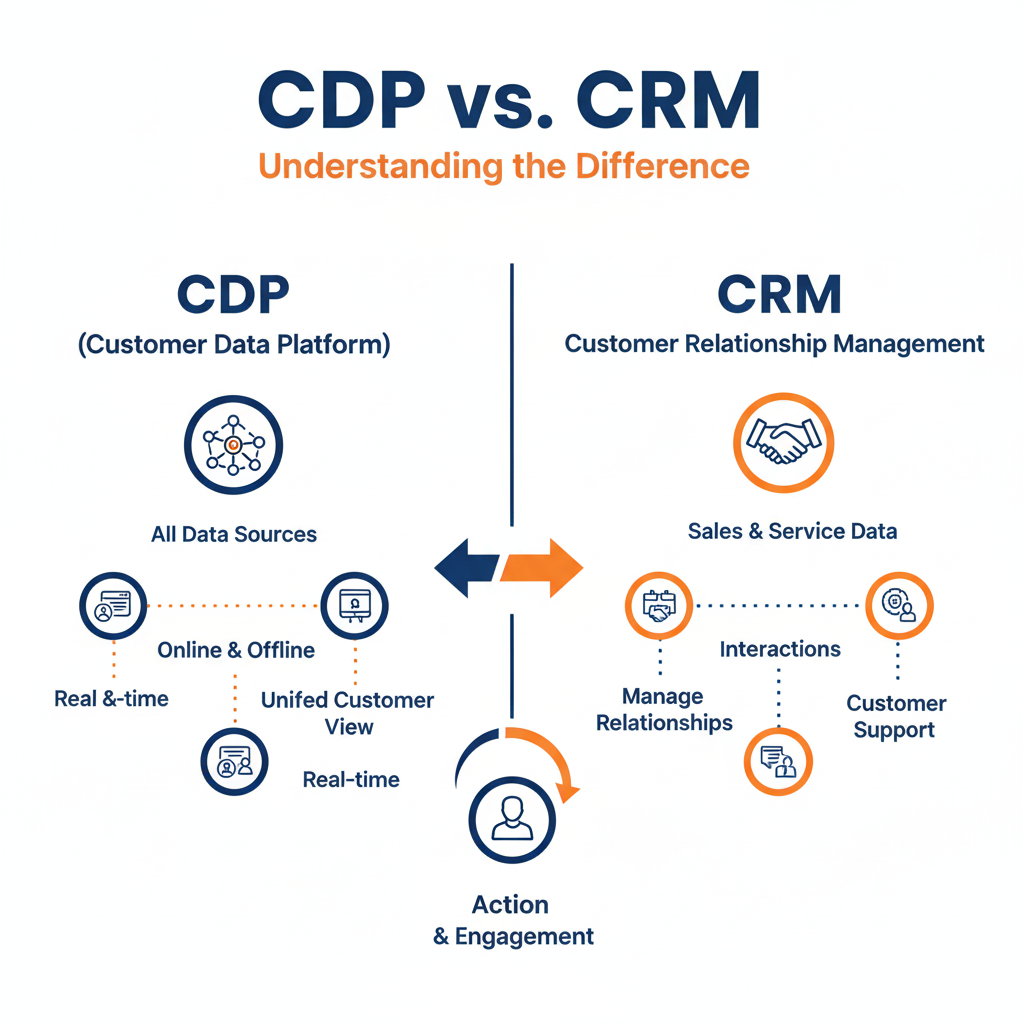
What Is a CRM (Customer Relationship Management)?
A CRM is a tool designed to manage direct relationships with customers and prospects — mostly focused on sales, service, and communication tracking.
🔍 Primary Purpose
To track interactions between your company and individual customers — emails, calls, meetings, purchases, or complaints.
💡 Key Functions
-
Store contact details (name, email, phone, company)
-
Track sales pipeline and deal stages
-
Manage lead nurturing and customer communication history
-
Provide insights for sales and support teams
-
Automate follow-ups and reminders
🧠 Example Tools
-
Salesforce
-
HubSpot CRM
-
Zoho CRM
-
Pipedrive
-
Microsoft Dynamics 365
🏁 Outcome
Improved sales productivity, customer retention, and relationship management.
What Is a CDP (Customer Data Platform)?
A CDP is a data integration and activation platform that collects, unifies, and activates customer data from multiple online and offline sources into a single customer profile.
🔍 Primary Purpose
To create a 360° view of each customer by combining behavioral, transactional, and demographic data — and make it actionable for marketing and personalization.
💡 Key Functions
-
Collect data from all touchpoints (website, app, social, CRM, email, offline)
-
Clean, deduplicate, and unify data into one customer ID
-
Segment customers in real time (based on behavior, intent, or attributes)
-
Integrate with marketing tools (email, ads, push notifications)
-
Enable AI-driven personalization and predictive analytics
🧠 Example Tools
-
Segment (by Twilio)
-
Tealium AudienceStream
-
Adobe Real-Time CDP
-
Treasure Data
-
mParticle
🏁 Outcome
Enhanced data-driven marketing, hyper-personalization, and real-time campaign activation.
Key Differences Between CDP and CRM
| Aspect | CRM (Customer Relationship Management) | CDP (Customer Data Platform) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Manage relationships and sales pipeline | Collect and unify customer data for analytics and activation |
| Data Type | Known, structured customer data (names, emails, sales) | Both known & anonymous data (cookies, device IDs, events, transactions) |
| Data Source | Mainly manual entry (sales, service interactions) | Automated from multiple sources (web, app, ads, CRM, POS, etc.) |
| Data Structure | Organized around individual contacts/leads | Organized around unified customer profiles |
| Primary Users | Sales, customer service teams | Marketing, analytics, data science teams |
| Goal | Improve sales efficiency and customer communication | Improve targeting, personalization, and customer experience |
| Integration | Limited to CRM & email systems | Integrates with martech stack (ads, email, analytics, etc.) |
| Real-Time Data | Often static or updated periodically | Real-time data ingestion and activation |
| AI Usage (2025) | Predictive sales scoring, lead prioritization | Predictive customer behavior, churn, and personalization |
| Example Outcome | “Who should my sales rep call next?” | “What personalized offer should this user see right now?” |
How CDP and CRM Work Together
The best-performing businesses in 2025 use both CRM and CDP together, not as alternatives but as complementary systems.
✅ Integration Workflow Example
-
CRM collects sales and service data (who the customer is, past purchases, support tickets).
-
CDP ingests this CRM data along with website behavior, ad interactions, and app usage.
-
CDP unifies everything into a single customer view.
-
Marketing teams use that unified data to run personalized campaigns across email, ads, and mobile.
-
CRM teams get context-rich profiles that help them prioritize and personalize follow-ups.
Example:
A user browses your website, adds a product to cart, but doesn’t buy.
The CDP tracks this in real time and triggers a personalized abandoned-cart email.
The CRM updates this user’s record, so a sales rep can follow up if needed.
When to Use Each
| Scenario | Recommended System |
|---|---|
| Tracking leads, calls, and sales deals | CRM |
| Unifying customer data across channels | CDP |
| Sending personalized marketing campaigns | CDP |
| Managing customer service tickets | CRM |
| Building behavioral audience segments | CDP |
| Analyzing sales team performance | CRM |
| Predicting churn or next best offer | CDP (AI/ML driven) |
CDP vs. CRM: The 2025 Marketing Shift
In 2025, marketers are shifting from CRM-driven sales to CDP-driven intelligence.
Here’s why:
-
Cookie deprecation demands first-party data strategies.
-
Personalization is now real-time and AI-powered.
-
Marketing automation needs clean, unified customer data.
-
Businesses require cross-channel orchestration — something CRMs alone can’t handle.
Hence, CDPs are becoming the central nervous system of marketing, while CRMs remain the heart of customer relationships.
Final Thoughts
To summarize:
| CDP = Marketing Brain | CRM = Relationship Heart |
|---|---|
| Gathers and analyzes data | Manages direct communication |
| Drives personalization and insights | Drives relationship and sales growth |
| Marketing-centric | Sales-centric |
In 2025 and beyond, the most successful brands integrate both:
-
CRM for building trust and nurturing relationships
-
CDP for powering data, personalization, and predictive intelligence
Together, they deliver a seamless customer experience across every touchpoint, turning fragmented data into meaningful, revenue-generating interactions.
Author



