Consumer behaviour refers to the study of how people — either individually or in groups — select, purchase, use, and dispose of goods, services, ideas, or experiences to satisfy their needs and wants.
In simpler terms, it’s about understanding why people buy what they buy, how they decide between brands, what influences their purchasing decisions, and how they feel before, during, and after a purchase.
Definition
Consumer behaviour is the process and activities that individuals or groups go through when selecting, purchasing, using, or disposing of products and services to fulfill their needs and desires.
It includes not just the act of buying, but also:
-
The mental process of evaluating options
-
The emotional triggers behind decisions
-
The social influences that shape choices
💡 Key Elements of Consumer Behaviour
-
What consumers buy – the product or service they choose
-
Why they buy it – the motivation behind the purchase
-
How they buy – the process or channels (online, offline, etc.)
-
When they buy – timing and frequency of purchases
-
Where they buy – store, website, or marketplace
-
How often they buy – loyalty, repeat purchases, or seasonal buying
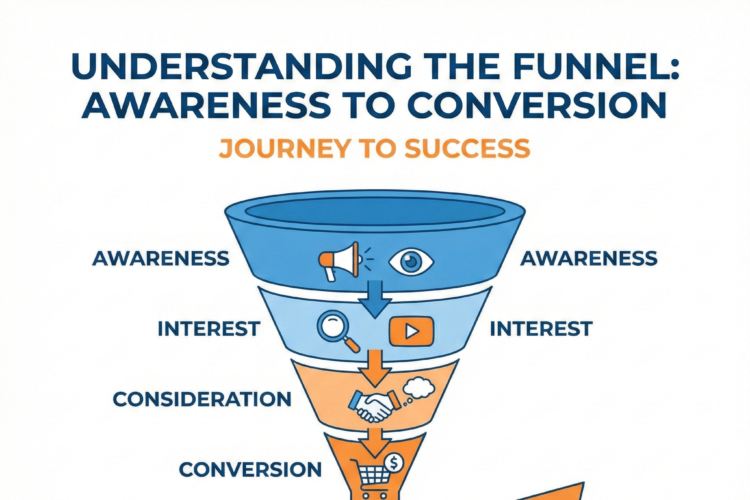
🔍 The Stages of Consumer Buying Process
Consumer behaviour typically follows five key stages:
1. Problem Recognition
The consumer realizes they have a need or a problem.
Example: “My old phone battery dies quickly — I need a new one.”
2. Information Search
They look for information about available options.
Example: Reading reviews, watching YouTube comparisons, or visiting stores.
3. Evaluation of Alternatives
They compare different brands, prices, features, and reviews.
Example: Comparing Samsung vs. iPhone vs. OnePlus.
4. Purchase Decision
They decide what to buy and from where.
Example: Buying an iPhone 15 from Apple’s online store.
5. Post-Purchase Behavior
After the purchase, they evaluate whether it met expectations.
Example: If satisfied, they may leave a positive review or recommend it to others.
🎯 Factors Influencing Consumer Behaviour
Consumer decisions are shaped by a combination of psychological, personal, social, and cultural factors.
1. Psychological Factors
-
Motivation – What drives the need (e.g., safety, comfort, status)
-
Perception – How consumers interpret marketing messages
-
Learning – Experience changes future buying behavior
-
Beliefs and Attitudes – Opinions and feelings toward brands
2. Personal Factors
-
Age & Lifestyle – Young adults vs. retirees have different buying patterns
-
Occupation & Income – Influences affordability and preferences
-
Personality & Self-Concept – Extroverts may prefer bold brands, introverts subtle ones
3. Social Factors
-
Family & Friends – Strong influence on choices
-
Social Class – Affects brand preferences
-
Influencers & Opinion Leaders – Drive trends and trust
4. Cultural Factors
-
Culture & Subculture – Shape values, norms, and habits
-
Traditions & Customs – Certain purchases align with festivals or rituals
-
Social Norms – Influence what’s acceptable or desirable
💬 Types of Consumer Buying Behavior
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Complex Buying Behavior | Involves high involvement and major differences between brands. | Buying a car or a house. |
| Dissonance-Reducing Buying Behavior | High involvement but few brand differences. | Buying an expensive washing machine. |
| Habitual Buying Behavior | Low involvement, little difference between brands. | Buying toothpaste or salt. |
| Variety-Seeking Buying Behavior | Low involvement but noticeable brand differences. | Trying different snack brands for fun. |
📈 Why Understanding Consumer Behaviour Is Important for Marketers
-
Improves Targeting and Segmentation
Helps marketers identify the right audience for their product. -
Enhances Product Development
Consumer insights guide brands to design products people actually need. -
Boosts Customer Retention
Understanding post-purchase behavior helps build loyalty. -
Optimizes Marketing Strategies
Knowing what motivates buyers helps in crafting emotional and persuasive campaigns. -
Predicts Market Trends
Studying consumer data helps forecast changes in demand and preferences. -
Improves Customer Experience (CX)
Brands can personalize communication, offers, and service based on buyer psychology.
🧩 Example in Action: Apple
Apple is a master at leveraging consumer behaviour:
-
Psychological Need: Status, innovation, and belonging.
-
Social Influence: Celebrity endorsements and community identity.
-
Post-Purchase Reinforcement: Exceptional product experience and ecosystem lock-in.
They don’t just sell phones — they sell a lifestyle identity.
🔮 The Future of Consumer Behaviour (2025 and Beyond)
-
AI-Driven Personalization: Brands will predict behavior using data analytics.
-
Sustainability Awareness: Eco-friendly and ethical choices will rise.
-
Omnichannel Journeys: Consumers will blend online and offline experiences seamlessly.
-
Social Proof Power: Reviews, influencers, and community feedback will dominate.
-
Emotion-Driven Marketing: Emotional connection will outweigh discounts.
🧭 In Summary
Consumer behaviour is the heart of all marketing.
It tells you:
-
What your customers want,
-
Why they want it, and
-
How to influence their decisions effectively.
By understanding consumer behaviour deeply, businesses can craft better products, create relevant campaigns, and build loyal relationships that last far beyond the first purchase.
Author